HashMap是存放键值对的集合,数据结构如下:
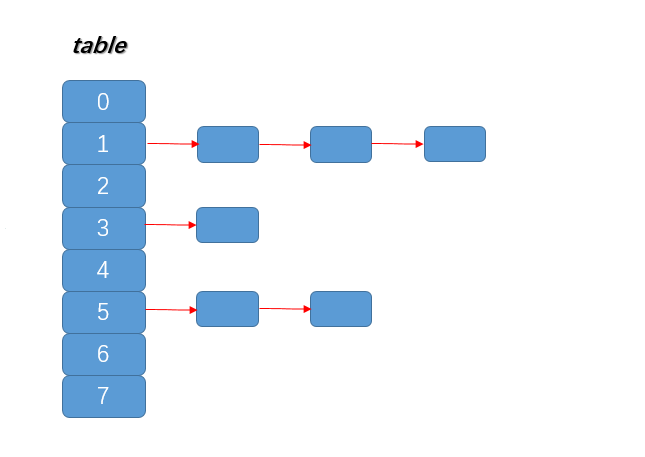
table被称为桶,大小(capacity)始终为2的幂,当发生扩容时,map容量扩大为两倍 HashMap采用拉链法解决Hash冲突,发生冲突时,新元素采用头插法插入到对应桶的链表中
HashMap有几个重要字段:
size:HashMap键值对的数量 capacity:桶数量,即table.length,默认16 loadFactor:负载因子,度量负载程度,基于时间和空间的权衡,默认0.75 threshold:阈值,当size>=threshold将发生扩容,threshold=capacity * loadFactor。
/**
* 默认初始容量 (必须是2的幂)
*/
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
/**
* 最大容量
*/
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
/**
* 默认负载因子
*/
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
/**
* 空表
*/
static final Entry[] EMPTY_TABLE = {};
/**
* hash table
*/
transient Entry[] table = (Entry[]) EMPTY_TABLE;
/**
* 键值对数目
*/
transient int size;
/**
* 阈值 (等于capacity * load factor).
*/
int threshold;
/**
* 负载因子
*/
final float loadFactor;
/**
* HashMap 结构性变化次数
* 用于快速失败
*/
transient int modCount;
static final int ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD_DEFAULT = Integer.MAX_VALUE; /**
* 构造函数
*/
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
threshold = initialCapacity;
init();
}
/**
* 构造函数,默认负载因子
*/
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
/**
* 构造函数,默认初始容量和负载因子
*/
public HashMap() {
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
/**
* 构造函数,通过map构造
*/
public HashMap(Map m) {
this(Math.max((int) (m.size() / DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR) + 1,
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY), DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
//初始化table
inflateTable(threshold);
//赋值到新map
putAllForCreate(m);
}Hash函数是获取对象处理后的hash值,为了让hash值散列更加均匀,减少碰撞,
扰动函数(Hash函数)对hashCode进行一些位运算。
/**
* 扰动函数(减少碰撞几率)
*/
final int hash(Object k) {
int h = hashSeed;
if (0 != h && k instanceof String) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
h ^= k.hashCode();
// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}确定桶下标的常用方式:hash % table.length,为了提高运行效率,
用位运算替代模运算。
能够这样做的前提,table.length必须是2的幂,这也是table的长度始终是2的幂的原因之一。
/**
* 确定桶下标
*/
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
// length必须是2的幂
return h & (length-1);
}
注意HashMap的值比较方法:e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))
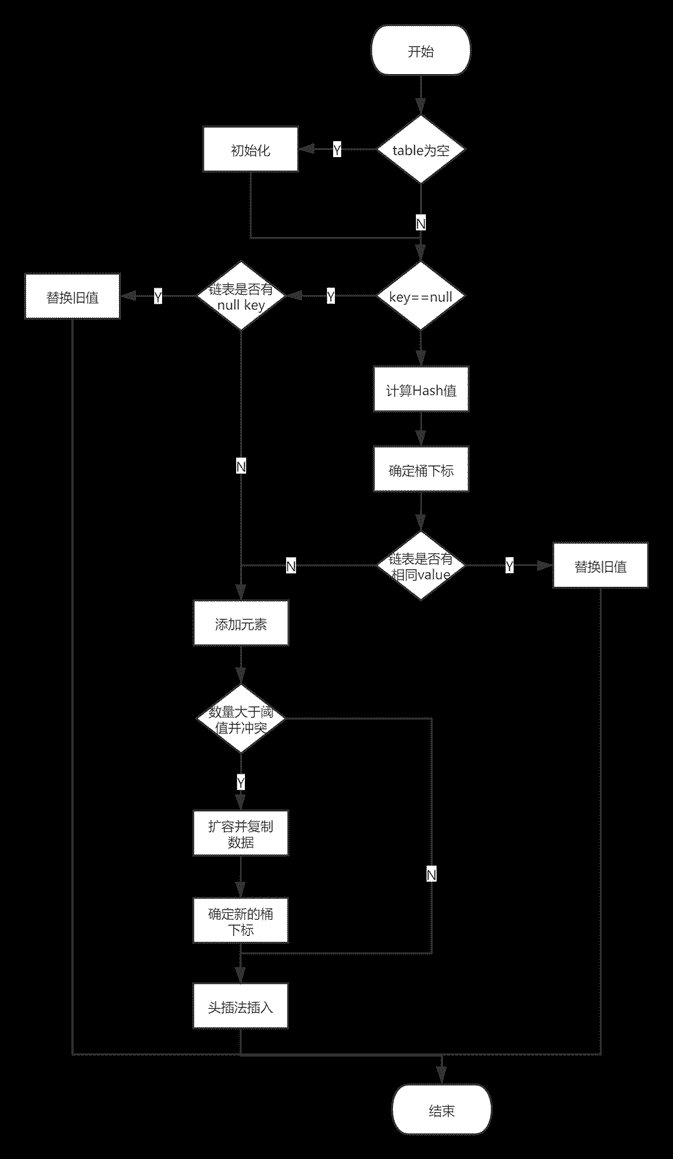
public V put(K key, V value) {
//空数组,则分配内存空间(延迟初始化)
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
//null键处理
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
//若key已经存在,则替换
for (Entrye = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
//比较值是否相同
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
//key不存在,则新增
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}HashMap的空间分配不是在构造函数中完成的,而是采用延迟初始化的方式,当第一个元素put时,才会进行空间分配。
private void inflateTable(int toSize) {
// Find a power of 2 >= toSize
int capacity = roundUpToPowerOf2(toSize);
threshold = (int) Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
//分配空间
table = new Entry[capacity];
initHashSeedAsNeeded(capacity);
}HashMap与HashTable的区别其中一点便是,前者key value都可以为null,后者都不能为null。
为null的键存放在table[0]中,即第一个桶。
/**
* null键插入
*/
private V putForNullKey(V value) {
/**
* null键存放在table[0]中(table[0]中不全是null键)
*/
for (Entrye = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
//计数增加
modCount++;
//添加Entry
addEntry(0, null, value, 0);
return null;
}当向HashMap添加一个不存在的key时(即size将增大),添加之前扩容检查。
扩容触发条件为:数量达到阈值并且发生Hash冲突。
扩容本质上,新建一个数组,使用头插法将旧map的元素拷贝到新map中。
添加键值对时,检验是否需要扩容。扩容的条件:数量达到阈值并且发生Hash冲突
/**
* 添加Entry
*/
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
//扩容条件:size大于阈值并且发生碰撞
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
//容量扩为2倍
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
//确定新桶下标
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}当扩容时:
容量已经达到最大值,仅调整阈值 容量未达到最大值,扩大table空间,并将旧map数据添加到新map中
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
//当容量达到最大时,仅调整阈值
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
//扩容
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
//数据复制
transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity));
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
}实际上,扩容本质是新建一个数组,然后在把数据复制过去,复制过程中,元素需要重新定位桶标
所以,多次扩容对性能影响很大
void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (Entrye : table) {
while(null != e) {
Entrynext = e.next;
if (rehash) {
e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);
}
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
}
}
}从Entry的构造函数中next = n;可以看出元素插入链表使用的头插法。
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
//table下标中第一个元素
Entrye = table[bucketIndex];
/**
* 构造方法中 next = e; 可见 使用的头插法插入到链表中
*/
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}
Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entryn) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
} /**
* 获取值
* 返回null有两种可能:1.不存在对应的键值对;2.存在key,但值为null
* 可以通过 {@link #containsKey containsKey} 进行区分
*/
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
//获取key为null的值
return getForNullKey();
Entryentry = getEntry(key);
return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue();
}
private V getForNullKey() {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
//可见,null的key存放在table[0]中,即第一个桶中
for (Entrye = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null)
return e.value;
}
return null;
}
final EntrygetEntry(Object key) {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);
//确定桶下标后,遍历链表
for (Entrye = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
//判断key是否相等。先比较的hash值,再比较的地址,最后比较equals
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
}
return null;
}