使用Lambda编程;可以简化很多代码;方便开发。
public class B {
private String id;
//用户id
private String userId;
//手机号
private String phone;
//ip地址
private String ip;
public B(String id, String userId, String phone, String ip) {
this.id = id;
this.userId= userId;
this.phone= phone;
this.ip = ip;
}
}
public class Test{
private static List<B> list = new ArrayList<>();
static {
B b = new B(;005;,;295;,;195;,;115;);
B b1 = new B(;007;,;295;,;197;,;115;);
B b2 = new B(;008;,;295;,;197;,;117;);
B b3 = new B(;009;,;296;,;198;,;119;);
B b4 = new B(;010;,;297;,;197;,;115;);
B b5 = new B(;011;,;297;,;197;,;111;);
B b6 = new B(;012;,;297;,;197;,;112;);
list.add(b);
list.add(b1);
list.add(b2);
list.add(b3);
list.add(b4);
list.add(b5);
list.add(b6);
}
}
以上面数据为例;此数据已处理;;需要查询用户手机号不同ip两条以上数据;前提确保userId、phone、ip相同数据只会出现一条;。
第一时间想到使用;Lambda分组的方式;通过userId和phone作为key
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, List<B>> collect = list.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(item -> item.getUserId() ; ;_; ; item.getPhone()));
for (Map.Entry<String, List<B>> map:collect.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(;key;;; map.getKey();;;size;;;map.getValue().size());
}
/** Output
* key;296_198;size;1
* key;295_197;size;2
* key;297_197;size;3
* key;295_195;size;1
*/
}
通过打印结果;可以清楚的看到每个分组下面有多少条数据。
然后我们只需要过滤出2条以上的数据。
public static void main(String[] args) {
list.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(item -> item.getUserId() ; ;_; ; item.getPhone()))
.entrySet()
.stream()
.filter(item -> item.getValue().size() >= 2)
.forEach(item -> {
List<B> value = item.getValue();
for (B b:value){
System.out.println(b.toString());
}
});
/** Output
* B{id=;007;, userId=;295;, phone=;197;, ip=;115;}
* B{id=;008;, userId=;295;, phone=;197;, ip=;117;}
* B{id=;010;, userId=;297;, phone=;197;, ip=;115;}
* B{id=;011;, userId=;297;, phone=;197;, ip=;111;}
* B{id=;012;, userId=;297;, phone=;197;, ip=;112;}
*/
}
对比一下原始数据是否正确
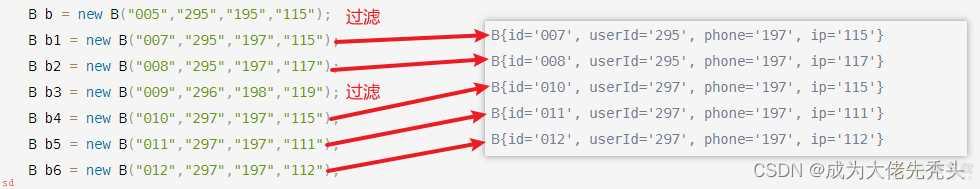
过滤的数据没问题;然后通过entrySet()遍历Map把这些数据提取出来;就能得到ip两条以上数据;使用flatMap()方法;进行重新组合;。
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<B> collect = list.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(item -> item.getUserId() ; ;_; ; item.getPhone()))
.entrySet()
.stream()
.filter(item -> item.getValue().size() >= 2)
.flatMap(item -> item.getValue().stream()).collect(Collectors.toList());
for (B b:collect) {
System.out.println(b.toString());
}
/** Output
* B{id=;007;, userId=;295;, phone=;197;, ip=;115;}
* B{id=;008;, userId=;295;, phone=;197;, ip=;117;}
* B{id=;010;, userId=;297;, phone=;197;, ip=;115;}
* B{id=;011;, userId=;297;, phone=;197;, ip=;111;}
* B{id=;012;, userId=;297;, phone=;197;, ip=;112;}
*/
}
这样就可以拿到完整List数据;如果你需要提取出这些集合中某一个数据;可以通过map()方法映射出字段。
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> collect = list.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(item -> item.getUserId() ; ;_; ; item.getPhone()))
.entrySet()
.stream()
.filter(item -> item.getValue().size() >= 2)
.flatMap(item -> item.getValue().stream())
.map(item->item.getId()).collect(Collectors.toList());
for (String id:collect) {
System.out.println(id);
}
/** Output
* 007
* 008
* 010
* 011
* 012
*/
}
后续你有其他处理;也很简单;只需要再后面追加你需要处理的方法即可。