vue2中props属性的使用是比较统一的基本就一种方式;但是vue3中其实方式是比较多的;因此就打算梳理一下。
会按照选项式和组合式进行梳理;包括属性的定义、取值以及属性的监听。
应该是叫单文件组件和组合式API;不知道vue官方是根据什么区分的。

这里大体上分为两大类进行说明;这两大类都需要使用defineProps来进行定义
const props = defineProps({
// 基础类型检查
// ;给出 ;null; 和 ;undefined; 值则会跳过任何类型检查;
propA: Number,
// 多种可能的类型
propB: [String, Number],
// 必传;且为 String 类型
propC: {
type: String,
required: true
},
// Number 类型的默认值
propD: {
type: Number,
default: 100
},
// 对象类型的默认值
propE: {
type: Object,
// 对象或数组的默认值
// 必须从一个工厂函数返回。
// 该函数接收组件所接收到的原始 prop 作为参数。
default(rawProps) {
return { message: ;hello; }
}
},
// 自定义类型校验函数
propF: {
validator(value) {
// The value must match one of these strings
return [;success;, ;warning;, ;danger;].includes(value)
}
},
// 函数类型的默认值
propG: {
type: Function,
// 不像对象或数组的默认;这不是一个工厂函数。这会是一个用来作为默认值的函数
default() {
return ;Default function;
}
}
})
这种方式还是比较简单的;基本和vue2没有太大的区别。
interface ganttChartItem {
// 宽度
width: number,
// 颜色
color: string
}
interface Props {
// id
id:string
// 宽度
width: number,
// 高度
height?: number,
// 是否初始化
init?: boolean,
// 子项
list?: Array<ganttChartItem>,
// 是否显示描述
desc?:string
// 描述颜色
descColor?:string
}
const props = withDefaults(defineProps<Props>(), {
// 高度默认20
height: 20,
// 默认初始化
init: true,
// 子项默认为空
list: () => [],
// 是否显示描述
desc: ;;,
// 描述颜色
descColor: ;;
});
特殊点;
泛型;可以通过定义interface接口来规范props的属性的格式。不像vue2中定义一个对象类型的属性;这个对象中可以有各种各样的子属性。?: 表示可选属性;:表示必填属性定义默认属性值时需要使用withDefaults取值时可以当成一个普通的对象;例如;
props.desc
watch(
() => props.visible,
(val) => {
open.value = val;
console.log(val);
}
);
<a-b v-model:visible=;show; />
//ab.vue
<template>
<div class=;container;>
<el-dialog v-model=;open; title=;Tips; width=;30%>
<span>This is a message</span>
</el-dialog>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang=;ts;>
import { watch, ref } from ;vue;;
const props = defineProps({
visible: {
type: Boolean,
default: false
}
});
const open = ref(false);
watch(
() => props.visible,
(val) => {
open.value = val;
console.log(val);
}
);
</script>
这里有个问题;虽然弹窗绑定的值可以直接是属性;但是好像不推荐这样使用
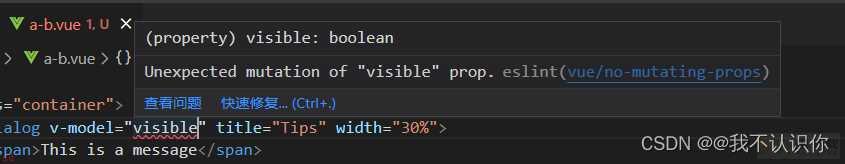
感觉setup语法糖模式用的更多一点;可能是我们公司用的比较多;。好久没这样用了;差点忘记怎么写了;
这个没什么说的;跟vue2一样
props: {
visible: {
type: Boolean,
default: false
}
},
使用时需要通过setup函数传参的方式来取值。
setup(props) {
return {
props
};
}
watch(
() => props.visible,
(val) => {
open.value = val;
console.log(val);
}
);
<template>
<div>
<el-dialog v-model=;open; title=;Tips; width=;30%>
<span>This is a message</span>
</el-dialog>
</div>
</template>
<script lang=;ts;>
import { defineComponent, watch, ref } from ;vue;;
export default defineComponent({
props: {
visible: {
type: Boolean,
default: false
}
},
setup(props) {
const open = ref(false);
watch(
() => props.visible,
(val) => {
open.value = val;
console.log(val);
}
);
return {
open
};
}
});
</script>
其实没必要非要用props属性;props属性应该在该用的时候用。
可以看一下我的这篇文章;vue3;使用ref和emit来减少props的使用
Vue3---Pinia-状态管理(环境搭建安装及各属性使用教程)详细使用教程
Vue3-Vite3-多环境配置---基于-vite-创建-vue3-全家桶项目(续篇)