Write a program to solve a Sudoku puzzle by filling the empty cells.
A sudoku solution must satisfy all of the following rules:
Each of the digits1-9 must occur exactly once in each row.
Each of the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each column.
Each of the the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each of the 9 3x3 sub-boxes of the grid.
Empty cells are indicated by the character '.'.
 求解
求解
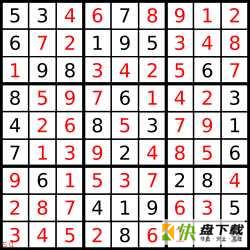 解答
解答
Note:
The given board contain only digits1-9 and the character '.'.
You may assume that the given Sudoku puzzle will have a single unique solution.
The given board size is always 9x9.
解法
数独游戏是一个经典的游戏,每一行、每一列和每一个小九格中填入1~9不重复的数字。
使用序号i=0~80遍历九宫格,再用y = i / 9; x = i % 9;转换成坐标。一般使用x和y坐标也可以,不过这样需要两重循环,递归起来也麻烦一点。
判断同一行、同一列中的数字都简单,判断同在一个小九格中有一个技巧,先计算xx = x / 3 * 3, yy = y / 3 * 3;,无论(x,y)是多少,(xx,yy)都是(x,y)所在的小九格中的左下角,从(xx,yy)出发,遍历小九格就比较容易了。
直接在原数组中记录答案,然后递归求解,如果解答失败,就把记录的该答案清空。这种方法在递归中经常用到,好处是不需要占用额外的内存,也不会产生”脏数据”干扰。
递归方法solveSudoku(char[][] board, int i)输入的位置i一定是没填的位置,查找下一个没填的位置k用这句话就行了while(++k < 81 && board[k / 9][k % 9] != '.') ;
算法如下,本算法击败了92%的java解法。
public static void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {
int k = -1;
while(++k < 81 && board[k / 9][k % 9] != '.') ;
if(k < 81) solveSudoku(board, k);
}
public static boolean solveSudoku(char[][] board, int i) {
int y = i / 9;
int x = i % 9;
for(char c = '1'; c <= '9'; c++) {
if(check(board, i, c)) {
board[y][x] = c;
int k = i;
while(++k < 81 && board[k / 9][k % 9] != '.') ;
if(k == 81) return true;
if(solveSudoku(board, k)) return true;
board[y][x] = '.';
}
}
return false;
}
public static boolean check(char[][] board, int index, char c) {
int y = index / 9;
int x = index % 9;
int xx = x / 3 * 3, yy = y / 3 * 3;
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
if(board[y][i] == c) return false;
if(board[i][x] == c) return false;
if(board[yy + i / 3][xx + i % 3] == c) return false;
}
return true;
}