

//
union和union all,你使用哪一个?
//
这是去年在线上遇到了一个系统负载的问题,问题的内容如下:某个从库上的系统负载从5天前开始,一直处于比较高的状态,磁盘IO也比较高,这里我先截取一部分监控的曲线图:
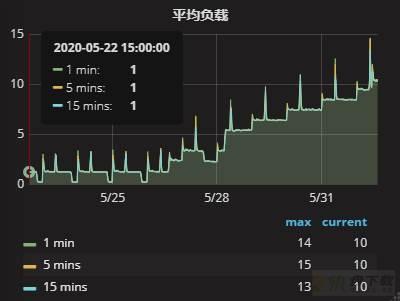
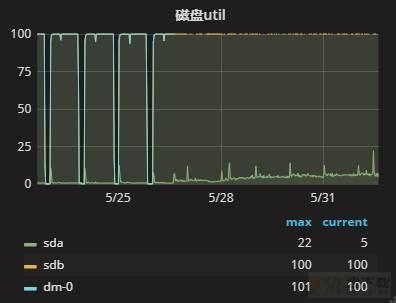
从监控上不难发现,该环境的系统负载成阶梯状线性提升,从5天前开始,逐渐增高,今天负载已经到达了10以上。磁盘的使用率也是从5天前开始,一直处于100%的状态。使用dstat的方法查看当前磁盘的状态,如下:
dstat -cdlmrtn --disk-util --top-io --top-latency 1 ----total-cpu-usage---- -dsk/total- ---load-avg--- ------memory-usage----- --io/total- ----system---- -net/total- sda--sdb-> usr sys idl wai hiq siq| read writ| 1m 5m 15m | used buff cach free| read writ| date/time | recv send|util:util> 0 1 49 50 0 0| 84M 872k|10.1 10.2 10.2|7365M 4320k 8389M 178M|2178 217 |01-06 14:51:10| 941B 1481B|5.70: 100> 1 1 46 52 0 0| 84M 0 |10.1 10.2 10.2|7365M 4312k 8390M 177M|2110 0 |01-06 14:51:11|1062B 2202B|23.1: 100> 1 1 48 50 0 0| 81M 1124k|10.1 10.2 10.2|7365M 4232k 8388M 179M|2145 280 |01-06 14:51:12|1042B 1336B| 0: 100> 1 1 48 50 0 0| 78M 0 |10.1 10.2 10.2|7365M 4232k 8387M 180M|2087 0 |01-06 14:51:13|4731B 3958B|4.50: 100> 1 1 47 51 0 0| 84M 980k|10.1 10.2 10.2|7365M 4248k 8384M 183M|2061 220 |01-06 14:51:14|4653B 17k|4.20: 100> 1 1 55 43 0 0| 82M 952k|10.1 10.2 10.2|7365M 4336k 8385M 182M|2204 186 |01-06 14:51:15|2638B 2844B|1.50: 100> 1 1 60 38 0 0| 74M 84k|10.1 10.2 10.2|7366M 4260k 8383M 183M|1936 7.00 |01-06 14:51:16|1102B 1356B|6.10: 100>
可以看到,磁盘(dsk/total)的read值非常高,达到了84MB/s,当前磁盘IO资源比较吃紧。
针对这个问题,我把我的分析思路写下来,希望会对大家有所帮助:
01
查看连接情况
登录到该机器上,使用show processlist的命令查看这个mysql实例的连接情况,可以看到如下的结果:
mysql--dba_admin@127.0.0.1:sys 11:22:16>>show processlist; +---------+-----------------+--------------------+--------+---------+---------+-------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+-----------+---------------+ | Id | User | Host | db | Command | Time | State | Info | Rows_sent | Rows_examined | +---------+-----------------+--------------------+--------+---------+---------+-------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+-----------+---------------+ | 2031512 | srv_datasync_ro | 10.xx.xxx.51:4619 | mygame | Query | 504168 | removing tmp table| select uid,s,g,t2,m from (select uid,s,g,t2,m from mygame_list_0 union select uid,s,g,t2,m from | 144 | 144 | | 2093843 | srv_datasync_ro | 10.xx.xxx.81:51287 | mygame | Query | 471115 | removing tmp table| select uid,s,g,t2,m from (select uid,s,g,t2,m from mygame_list_0 union select uid,s,g,t2,m from | 144 | 144 | | 2259357 | srv_datasync_ro | 10.xx.xxx.31:7982 | mygame | Query | 384715 | executing | select uid,s,g,t2,m from (select uid,s,g,t2,m from mygame_list_0 union select uid,s,g,t2,m from | 0 | 0 | | 2294662 | srv_datasync_ro | 10.xx.xxx.63:52149 | mygame | Query | 366218 | executing | select uid,s,g,t2,m from (select uid,s,g,t2,m from mygame_list_0 union select uid,s,g,t2,m from | 0 | 0 | | 2298410 | srv_datasync_ro | 10.xx.xxx.75:31859 | mygame | Query | 364181 | executing | select uid,s,g,t2,m from (select uid,s,g,t2,m from mygame_list_0 union select uid,s,g,t2,m from | 0 | 0 | | 2421697 | srv_datasync_ro | 10.xx.xxx.78:64434 | mygame | Query | 298299 | executing | select uid,s,g,t2,m from (select uid,s,g,t2,m from mygame_list_0 union select uid,s,g,t2,m from | 0 | 0 | | 2584289 | srv_datasync_ro | 10.xx.xxx.60:39386 | mygame | Query | 211911 | executing | select uid,s,g,t2,m from (select uid,s,g,t2,m from mygame_list_0 union select uid,s,g,t2,m from | 0 | 0 | | 2746619 | srv_datasync_ro | 10.xx.xxx.51:28107 | mygame | Query | 125515 | executing | select uid,s,g,t2,m from (select uid,s,g,t2,m from mygame_list_0 union select uid,s,g,t2,m from | 0 | 0 | | 2906024 | srv_datasync_ro | 10.xx.xxx.54:8190 | mygame | Query | 39114 | executing | select uid,s,g,t2,m from (select uid,s,g,t2,m from mygame_list_0 union select uid,s,g,t2,m from | 0 | 0 | | 2975370 | srv_datasync_ro | 10.xx.xxx.37:60255 | mygame | Query | 1643 | executing | select uid,s,g,t2,m from (select uid,s,g,t2,m from mygame_list_0 union select uid,s,g,t2,m from | 0 | 0 | | 2975827 | srv_datasync_ro | 10.xx.xxx.61:36801 | NULL | Sleep | 1088 | | NULL | 0 | 0 | +---------+-----------------+--------------------+--------+---------+---------+-------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+-----------+---------------+ | 0 | 0 |
从上面的show processlist结果,可以看到以下几条信息:
1、
1、state列的状态有2种,一种是executing,另外一种是removing tmp table,从这里的状态不难看出,该查询使用了内存临时表
2、time字段的最大值为504168,这个值说明有些select查询已经hang在这里了,time的值代表已经执行了这么多秒(依旧没有拿到结果),我们以id为2031512这一行为例,它的Time值是504168,进行简单的时间单位换算:
mysql> select 504168/3600/24; +----------------+ | 504168/3600/24 | +----------------+ | 5.83527778 | +----------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
可以看到,这个连接,其实是5天前的连接了,也就是说,这个SQL已经执行了5天,一直卡在这个removing tmp table的界面没有返回。这样算起来,似乎和发现故障的时间比较吻合,以这个信息为切入点,我问业务方要了下执行的SQL语句。
3、并发的SQL语句看起来都是一样的,只有time字段在递减,这表示之前的一个SQL执行的时间太长了,导致后续的SQL都卡在这里了,由于后续的SQL也进入了executing状态,也占用了一部分MySQL的资源,又反向影响之前的SQL,导致之前的SQL迟迟拿不到返回结果。
02
确认业务方的SQL语句
经过和业务方沟通,拿到了业务方执行的SQL语句,具体的表名字和数据库名字不写了,这里简单说下这个SQL的情况,它是对20个表的一个union查询,类似:
select * from t1 union
select * from t2 union
...
select * from t20;
其中,单表的数据量有200w。所有表加起来在磁盘上的文件大小总共是5G。
使用explain查看执行计划,发现对20个表做的都是全表扫描,最后还有个using temporary table 的字样,也就是使用了临时表。
从这个负载上升的阶梯状图形,大概能猜到,这个任务是每天执行一次,将所有的表数据通过union的方式查到,然后推送给前端。但是很明显,这样的操作使用了内存临时表,导致执行时间过长,是有问题的。
看到这里,系统负载这张图就比较容易看懂了:

每一天的任务还没有执行完成,第二天的任务就来了,这样一天一天累计,系统的负载也就慢慢上来了。
03
尝试修改MySQL部分参数
看到执行的命令迟迟得不到返回,而且可以确定,整个union的过程使用了临时表,于是我习惯性的修改了MySQL的几个参数:
1、调大buffer pool size的值;
2、调整innodb_thread_concurrency值为一个更大的值,让它兼容更多的并发查询数
3、调整tmp_table_size的值,让临时表容量变得更大点儿
等待了数十分钟之后,发现问题依旧没有得到解决。
04
尝试kill这几个查询线程
因为业务方对数据的读取采用的是快照读,所以不牵扯大事务回滚的情况,我使用kill queryid的方法对其中的几条select进行了kill操作,发现一个现象。
| 2975370 | srv_datasync_ro | 10.xx.xxx.37:60255 | mygame | Query | 1643 | executing kill query 2975370; | 2975370 | srv_datasync_ro | 10.xx.xxx.37:60255 | Killed | Query | 1683 | removing tmp table
kill操作之后,状态从query变为killed,连接的状态从executing变为removing tmp table,但是并没有释放连接。
关于kill + queryid这个命令到底做了什么操作,大家可以查看一周前的文档,里面有比较详细的说明。目前我们需要了解该命令的本质是:
0、kill + queryid命令等于kill + connection +queryid
1、它将那个session的状态改为kill_connection,此时MySQL会进行判断,如果一个连接线程的状态为kill_connection,那么MySQL会将其Command列改为killed
2、关掉该查询线程的网络连接,等待innodb识别到该线程的状态为kill_connection,进行资源回收。
05
重启MySQL服务
因为是在从库上进行的SQL操作,而且目前负载过大,磁盘IO打满,整个库几乎处于不可用状态,为了快速解决问题,我直接进行了重启MySQL服务的操作。
注意,如果是主库,请不要直接执行停库动作,除非的你的环境已经有了HA的保障。
重启服务的时候,为了让整个重启的过程更加平滑,可以提前调整参数:innodb_max_dirty_pages_pct.
我们可以使用set global variables的方法临时设置这个参数的值为0,那么就意味着动态的慢慢主动将buffer pool中的脏页刷回磁盘,而不是通过关闭MySQL被动刷新,这个参数的默认值是75,也就是说,最大的脏页最多可以占用buffer_pool中75%空间。我们可以通过查看show engine innodb status命令中的modified db pages,等到这个值很小的时候,我们就可以关闭数据库了,这个时候关闭数据库的速度就会很快。
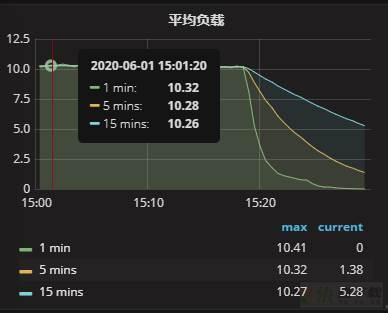
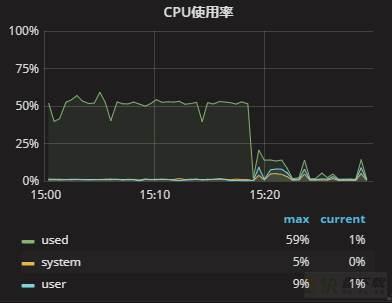
整个重启过程还算顺利,关闭MySQL和开启MySQL服务分别用了30s左右,整个过程耗时1min左右。重启服务之后,效果还是很明显的,监控如下:
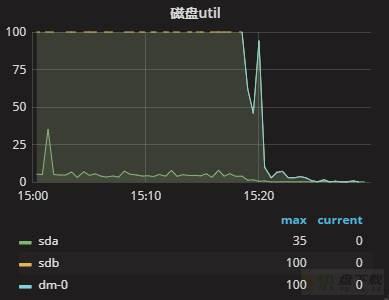
06
对union这个SQL的优化
经过跟业务方进行沟通,发现了这个业务的几个特点:
1、所有的20个表都是状态表,每个表平均200w数据,每天这些数据都会更新和新增,也就是update和insert
2、这个任务每天运行一次,之前每次运行的时长是数个小时,最近数据量增加了,运行时间越来越长。
3、数据是用uid维度进行插入的,理论上不存在重复的数据,注意,这条很关键。
既然不存在重复,那么应用union这个连接方法,似乎就有点不妥。
我们知道,union对两个表进行联合查询的时候,会进行一个去重的操作,而union all进行联合查询的时候,会将所有的数据都给罗列出来。现在看起来,似乎是所有表的数据在提取的时候,有个去重的操作,导致这个SQL的执行时间变长了。为了验证这个过程,我进行了一组测试:
mysql yeyztest>>create table test_union (id int); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec) mysql yeyztest>>insert into test_union values (1),(2),(3); Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.01 sec) Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql yeyztest>>select 4 as f union select id from test_union; +------+ | f | +------+ | 4 | | 1 | | 2 | | 3 | +------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql yeyztest>>explain select 4 as f union select id from test_union; +----+--------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+--------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------+ | 1 | PRIMARY | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | No tables used | | 2 | UNION | test_union | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 100.00 | NULL | | NULL | UNION RESULT | <union1,2> | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | Using temporary | +----+--------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------+ 3 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec) mysql yeyztest>>explain select 4 as f union all select id from test_union; +----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------+ | 1 | PRIMARY | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | No tables used | | 2 | UNION | test_union | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 100.00 | NULL | +----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------+ 2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
经过这个测试,可以看到,使用union all的方法进行联合查询的时候,执行计划结果只有2行,是没有using temporary的字样的。也就是说,不会出现内存临时表。而使用union查询的时候,执行计划有3行,而且第三行里面有明显的using temporary table字样,这一点,可能是这个SQL的一个重要优化点。
其实,在MySQL中,还可以使用union distinct来显示的指定union查询去重,union distinct语法和单独union的语法执行结果是一样的,只不是加了distinct之后,更加容易理解。如下:
mysql> select 1 union select 1 union select 1; +---+ | 1 | +---+ | 1 | +---+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select 1 union distinct select 1 union distinct select 1; +---+ | 1 | +---+ | 1 | +---+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select 1 union all select 1 union all select 1; +---+ | 1 | +---+ | 1 | | 1 | | 1 | +---+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
07
将业务SQL改写为union all的方法重试
经过了上面的测试,跟业务方协商,将SQL改为了union all的方法手工执行了一两次,也就是从:
select * from t1 union
select * from t2 union
...
select * from t20
改为:
select * from t1 union all
select * from t2 union all
...
select * from t20 ;
重新测试这个数据联合查询的SQL,发现执行时间从之前的数个小时变为了7分钟。性能整整提高了好几百倍。
监控图像也变为了:
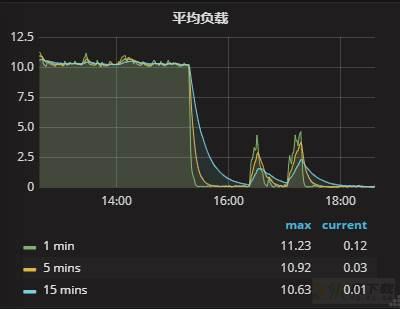
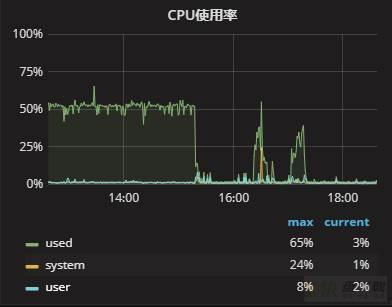
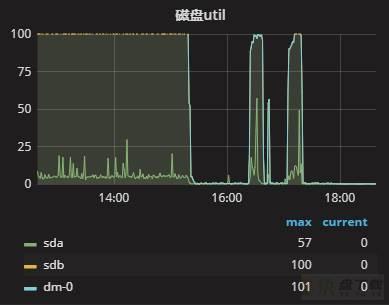
从这个图像上不难看出,每次执行SQL期间,负载有些许上升,但是整体可控,查询的整个过程呈现周期性。
这个案例给了我几点启发:
业务侧:
1、大表连接查询的时候,尽量不要使用union 的操作,因为union的操作要进行去重,所以会进行重复值的判断,这个判断过程消耗CPU和磁盘IO比较严重
2、可以使用union all的方法代替union的方法,当然,如果表特别大,不建议使用union的方式进行查询,还是建议拆分成单个表进行查询,然后再汇总结果
3、如果表中的字段有时间字段,定时任务取每天的增量数据可能比全量数据更加容易一些。
DB侧:
1、可以使用pt-kill来限制最长查询时间,一旦某个查询超过这个时间阈值,就直接kill掉查询,防止拖垮整个数据库。
2、对于服务器的监控还是需要完善,负载长时间处于较高位置,或者IO util值持续10分钟达到100%,就应该报警,而不是故障驱动,被动发现。