什么是 CSSCSS的基本规则CSS的引入规则内部样式外部样式内联样式 选择器标签选择器类选择器id选择器通配符选择器后代选择器子选择器并集选择器伪类选择器 元素属性设置字体属性文本属性背景属性圆角矩形 块级元素和行内元素盒模型块级元素的水平居中浏览器默认样式的去除 弹性布局
CSS;即 Cascading Style Sheets;层叠样式表;它是一种用来表现html或xml等文件样式的计算机语言;通过使用CSS;可以精确控制网页中元素的位置及样式;使页面更加美观。
CSS在html文件中的书写位置是在style标签中;html对style标签的位置没有特殊规定;即可以是页面的任意位置;一般习惯放在head标签内;style标签中的代码就是CSS的;必须遵循CSS的语法规则;CSS不区分大小写;但一般默认使用小写字母;CSS中的冒号之后一般带有一个空格;
即在html文件的style标签中;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang=;en;>
<head>
<meta charset=;UTF-8;>
<meta http-equiv=;X-UA-Compatible; content=;IE=edge;>
<meta name=;viewport; content=;width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0;>
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div{color: blue;
font-size: 30px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>hello css!</div>
</body>
</html>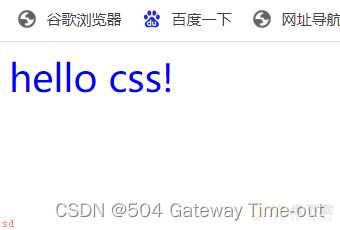
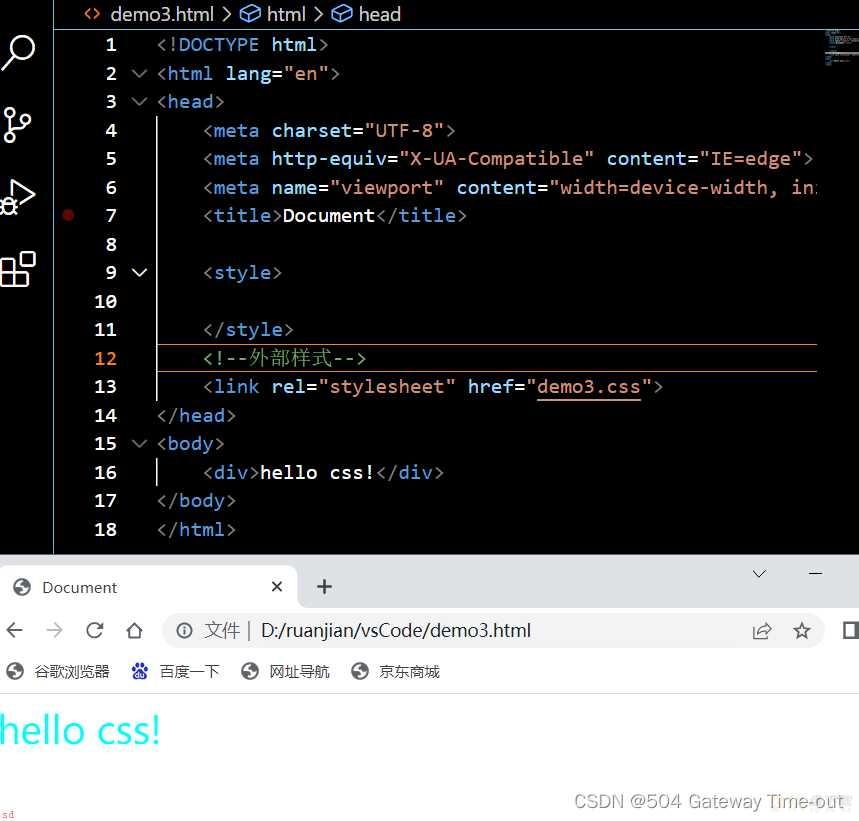
外部样式即首先在当前html文件外创建一个CSS文件;然后使用link标签引入这个CSS文件;
即在元素中使用style标签;写入CSS内容;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang=;en;>
<head>
<meta charset=;UTF-8;>
<meta http-equiv=;X-UA-Compatible; content=;IE=edge;>
<meta name=;viewport; content=;width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0;>
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div{color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--会覆盖上面的样式设置-->
<div style=;color: green; font-size:30px;>hello css!</div>
</body>
</html>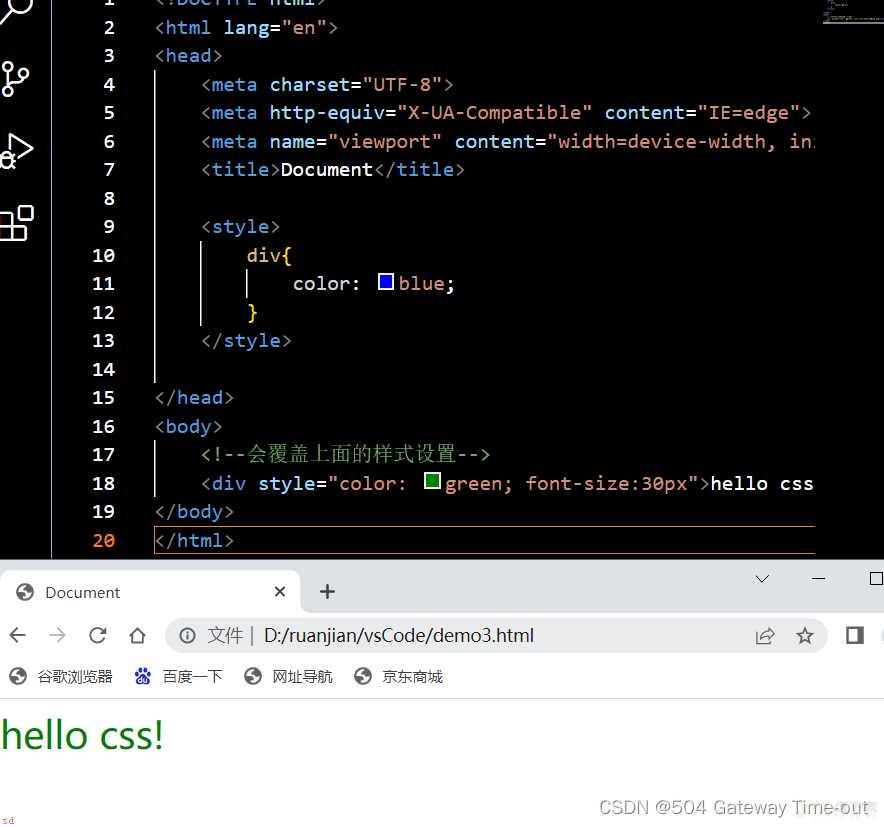
CSS中的选择器分为基本选择器和复合选择器;首先是基础选择器;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang=;en;>
<head>
<meta charset=;UTF-8;>
<meta http-equiv=;X-UA-Compatible; content=;IE=edge;>
<meta name=;viewport; content=;width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0;>
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div {
color: blue;
font-size: 20px;
}
p {color:aqua;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>hello world !</div>
<p>hello css !</p>
</body>
</html>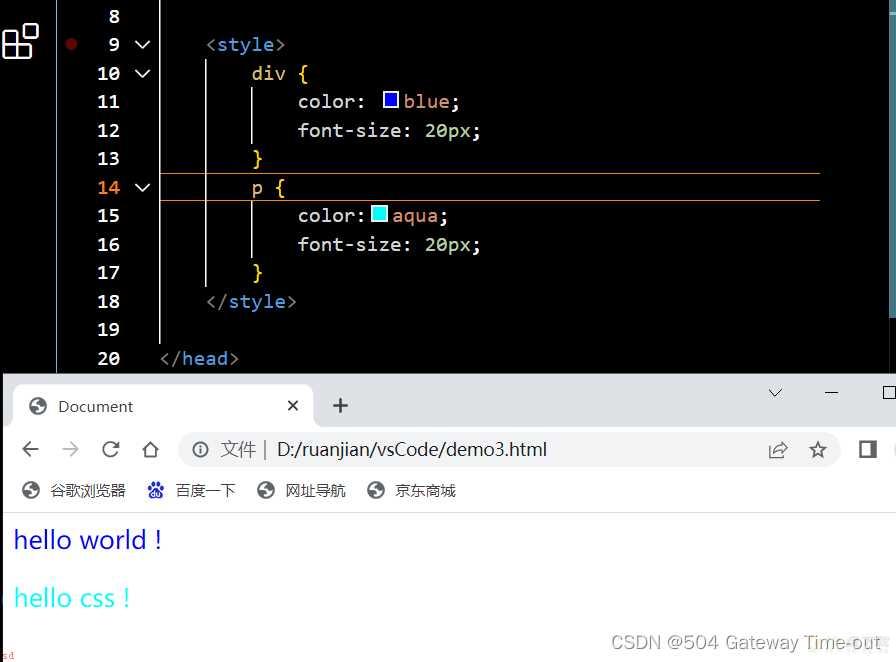
使用标签选择器可以同时对同一类型的标签进行选择;来同时设置同类型标签内容的样式;
但是标签选择器会带来的问题是;无法进行差异化选择;因此引入了类选择器;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang=;en;>
<head>
<meta charset=;UTF-8;>
<meta http-equiv=;X-UA-Compatible; content=;IE=edge;>
<meta name=;viewport; content=;width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0;>
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.one{color: blue;
font-size: 20px;
}
.two{color: blueviolet;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class=;one;>hello world !</div>
<p class=;two;>hello css !</p>
</body>
</html>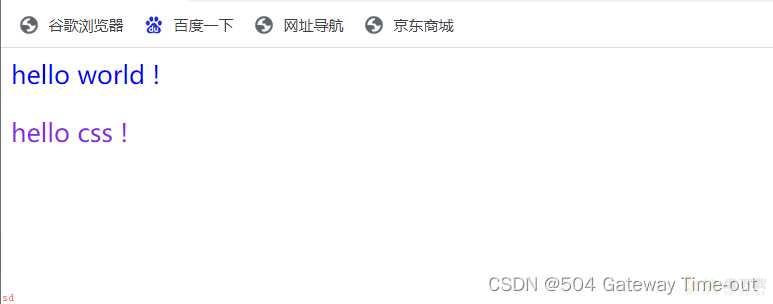
类选择器是以点 . 开头;后面是类选择器的名称;名称任意;
调用类选择器时;使用class属性;
一个类选择器可以被多个标签使用;一个标签中也可以有多个类选择器;中间以空格隔开;
使用类选择器可以进行差异化选择;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang=;en;>
<head>
<meta charset=;UTF-8;>
<meta http-equiv=;X-UA-Compatible; content=;IE=edge;>
<meta name=;viewport; content=;width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0;>
<title>Document</title>
<style>
#one{color: blue;
font-size: 20px;
}
#two{color: blueviolet;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id=;one;>hello world !</div>
<div id=;two;>hello css !</div>
</body>
</html>
id选择器以#开头;
调用id选择器时使用id属性;
id作为一种身份标识;不可以被多个标签共同使用;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang=;en;>
<head>
<meta charset=;UTF-8;>
<meta http-equiv=;X-UA-Compatible; content=;IE=edge;>
<meta name=;viewport; content=;width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0;>
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {color: red;
font-size: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>好好学习,天天向上</div>
</body>
</html>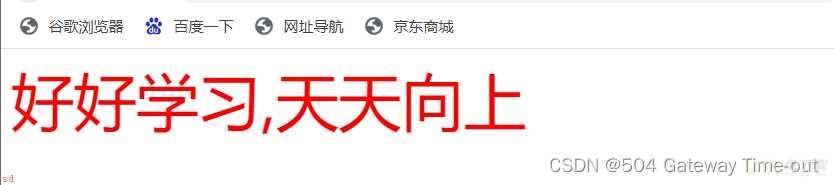
使用通配符选择器;可以选择所有标签进行设置;
下面是复合选择器;
复合选择器是对基础选择器的组合;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang=;en;>
<head>
<meta charset=;UTF-8;>
<meta http-equiv=;X-UA-Compatible; content=;IE=edge;>
<meta name=;viewport; content=;width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0;>
<title>Document</title>
<style>
ol li {color: blue;
font-size: 30px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ol>
<li>万事如意</li>
<li>平安喜乐</li>
</ol>
<ul>
<li>生活顺利</li>
<li>得偿所愿</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
后代选择器;即选择一个元素的某个子元素;也可以选择这个子元素的子元素;
两个元素之间要有空格隔开;否则不构成后代选择器;
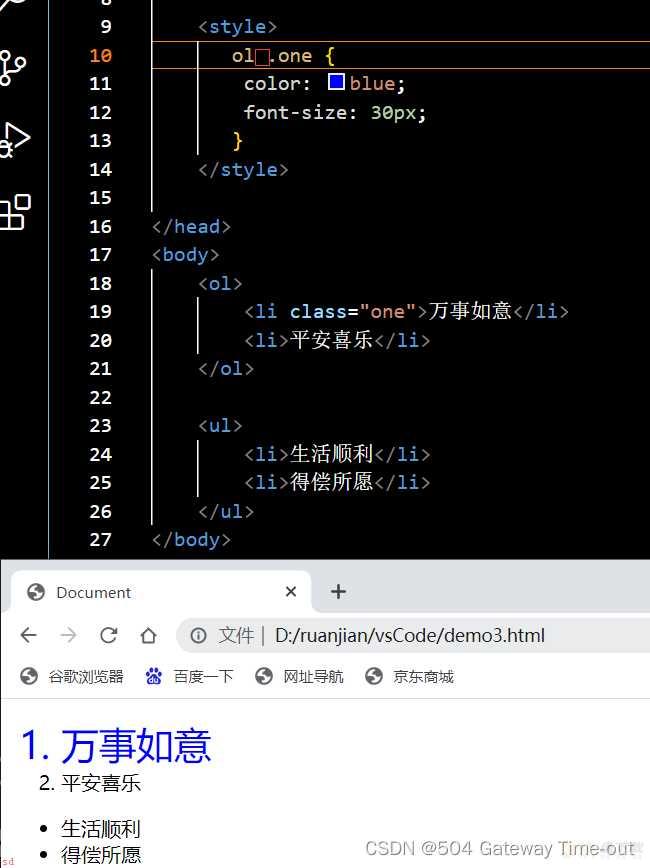 如上图;红色方框的位置必须有空格;否则不构成后代选择器;设置就不会生效;
如上图;红色方框的位置必须有空格;否则不构成后代选择器;设置就不会生效;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang=;en;>
<head>
<meta charset=;UTF-8;>
<meta http-equiv=;X-UA-Compatible; content=;IE=edge;>
<meta name=;viewport; content=;width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0;>
<title>Document</title>
<style>
ul>li {color: blue;
font-size: 30px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ol>
<li>万事如意</li>
<li>平安喜乐</li>
</ol>
<ul>
<li>生活顺利</li>
<li>得偿所愿</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
子选择器与后代选择器基本相同;但是子选择器只能选择某个元素的子类元素;对子类元素的子类元素不生效;
使用大于号来分隔元素与子元素
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang=;en;>
<head>
<meta charset=;UTF-8;>
<meta http-equiv=;X-UA-Compatible; content=;IE=edge;>
<meta name=;viewport; content=;width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0;>
<title>Document</title>
<style>
ul,ol {color: blue;
font-size: 30px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ol>
<li>万事如意</li>
<li>平安喜乐</li>
</ol>
<ul>
<li>生活顺利</li>
<li>得偿所愿</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>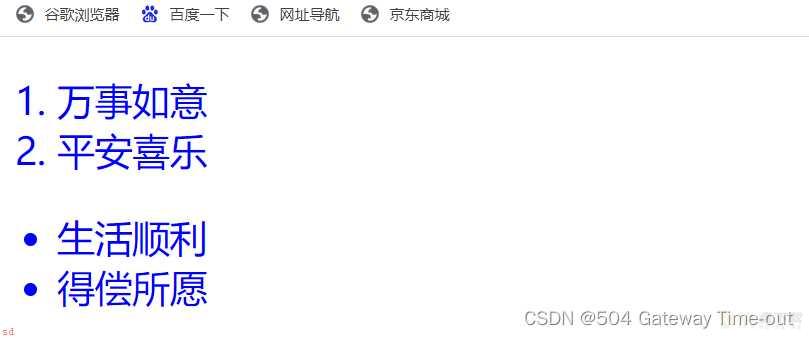
并集选择器适用于多组标签同时设置;
并集选择器的元素之间使用逗号分隔;
关于css的伪类选择器实际有多种类型;这里只简单的介绍2种;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang=;en;>
<head>
<meta charset=;UTF-8;>
<meta http-equiv=;X-UA-Compatible; content=;IE=edge;>
<meta name=;viewport; content=;width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0;>
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div:hover{color: red;
}
p:active{color: aqua;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>hello css!</div>
<p>hello world!</p>
</body>
</html>标签名;hover,当鼠标悬停在元素上时;生效;
标签名;active;鼠标按下但未弹起时生效;
字体样式设置;font-family属性
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang=;en;>
<head>
<meta charset=;UTF-8;>
<meta http-equiv=;X-UA-Compatible; content=;IE=edge;>
<meta name=;viewport; content=;width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0;>
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.one {font-family: ;Microsoft YaHei;;
}
.two {font-family: ;宋体;;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class=;one;>微软雅黑</div>
<div class=;two;>宋体</div>
</body>
</html>
设置字体大小;font-size属性;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang=;en;>
<head>
<meta charset=;UTF-8;>
<meta http-equiv=;X-UA-Compatible; content=;IE=edge;>
<meta name=;viewport; content=;width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0;>
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.one {font-size: 20px;
}
.two {font-size: 30px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class=;one;>hello</div>
<div class=;two;>good</div>
</body>
</html>
字体粗细;font-weight:
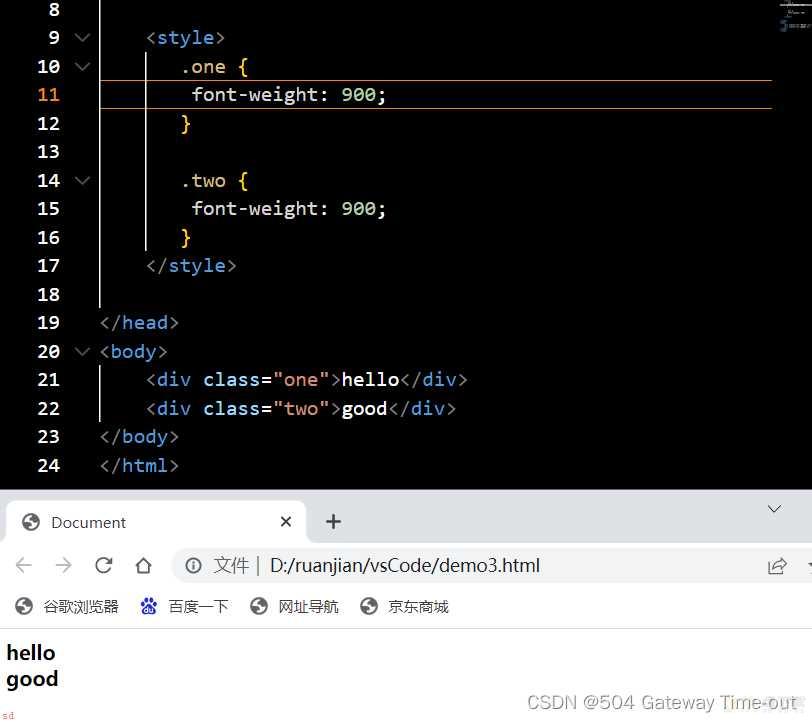
字体粗细可以使用font-weight来设置;
字体粗细可以使用数字来表示;取值范围为100-900;
当设置为normal,表示不加粗;
字体倾斜:font-style
<style>
.one {/*倾斜*/
font-style: italic;
}
.two {/*不倾斜*/
font-style: normal;;
}
</style>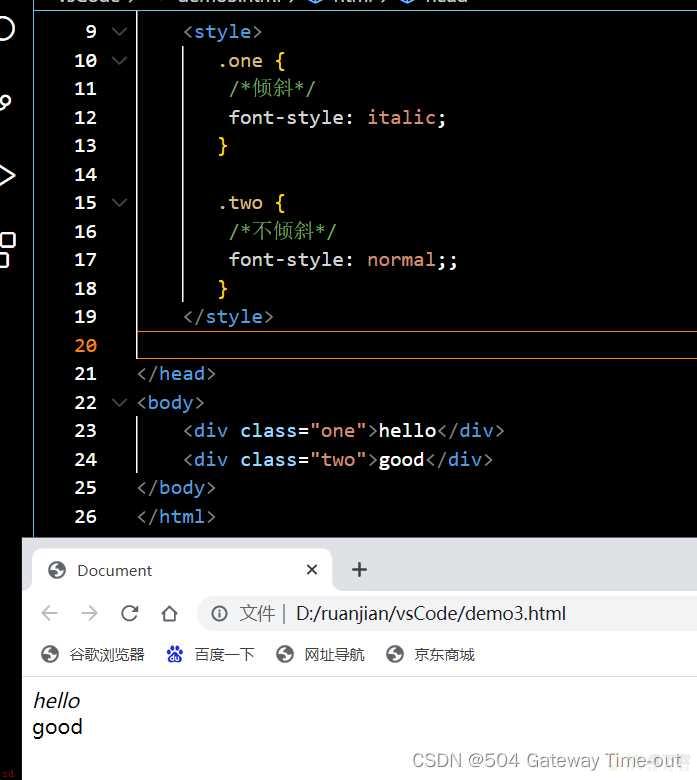
文本颜色;color
文本颜色的设置主要有3种方式;
直接使用颜色的英文单词;使用十六进制来表示;使用RGB方式;通过对R (red), G (green), B (blue)设置不同的分量大小;来得到不同的颜色 ;;
<style>
.one {color: blue;
}
.two {color: #ff4567;
}
.three {/*rgb分量的取值范围是0-255*/
color: rgb(110,120,119);
}
</style>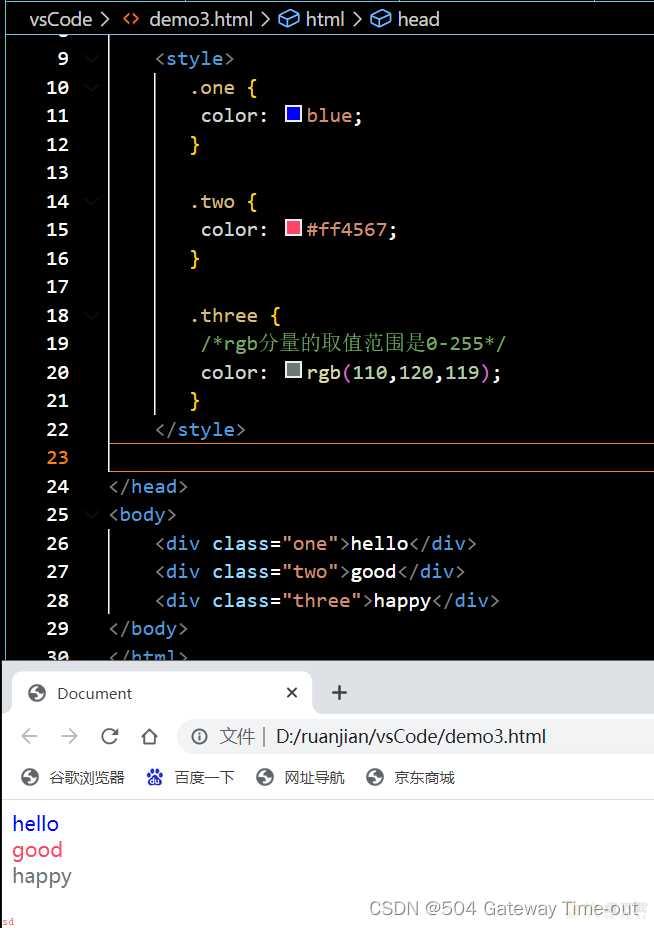 文本对齐;text-align
文本对齐;text-align
这里的文本广泛代表图片等元素;
<style>
.one {/*左对齐*/
text-align: left;
}
.two {/*居中对齐*/
text-align: center;
}
.three {/*右对齐*/
text-align: right;
}
</style>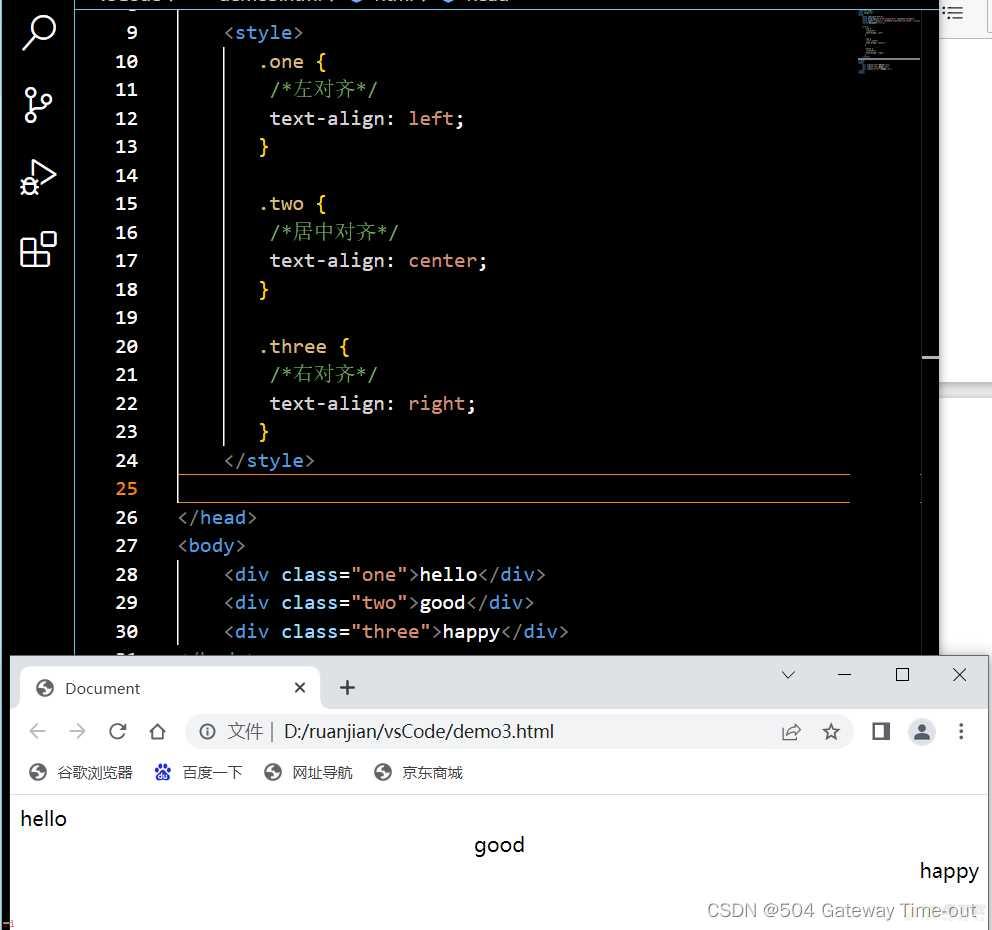 文本装饰;text-decoration
文本装饰;text-decoration
<style>
.one {/*上划线*/
text-decoration: overline;
}
.two {/*下划线*/
text-decoration: underline;
}
.three {/*没有任何操作;可以用来删除下划线*/
text-decoration: none;
}
.four {/*删除线*/
text-decoration: line-through;
}
</style>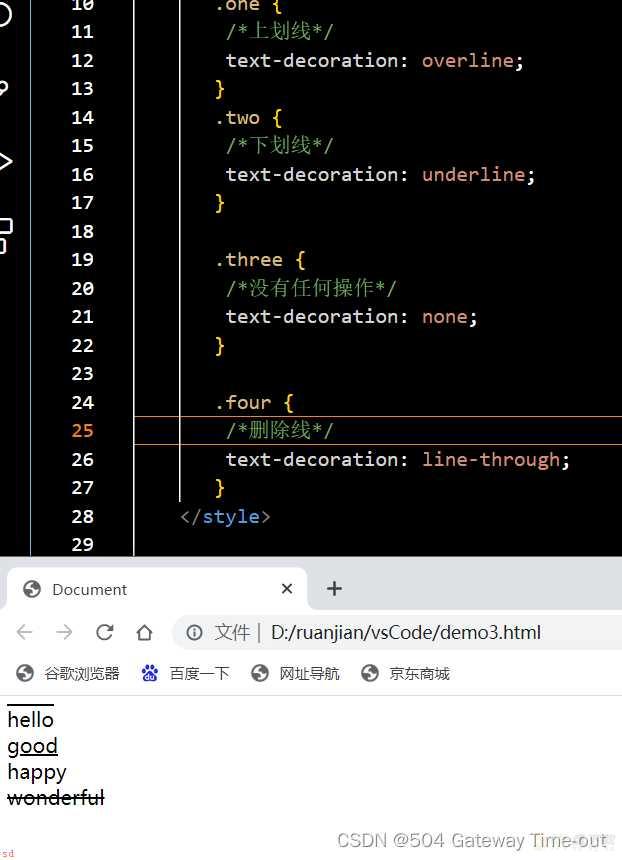
文本缩进;text-indent
<style>
.one {/*向右缩进;正值*/
text-indent: 2em;
}
.two {/*向左缩进;负值*/
text-indent: -2em;
}
</style>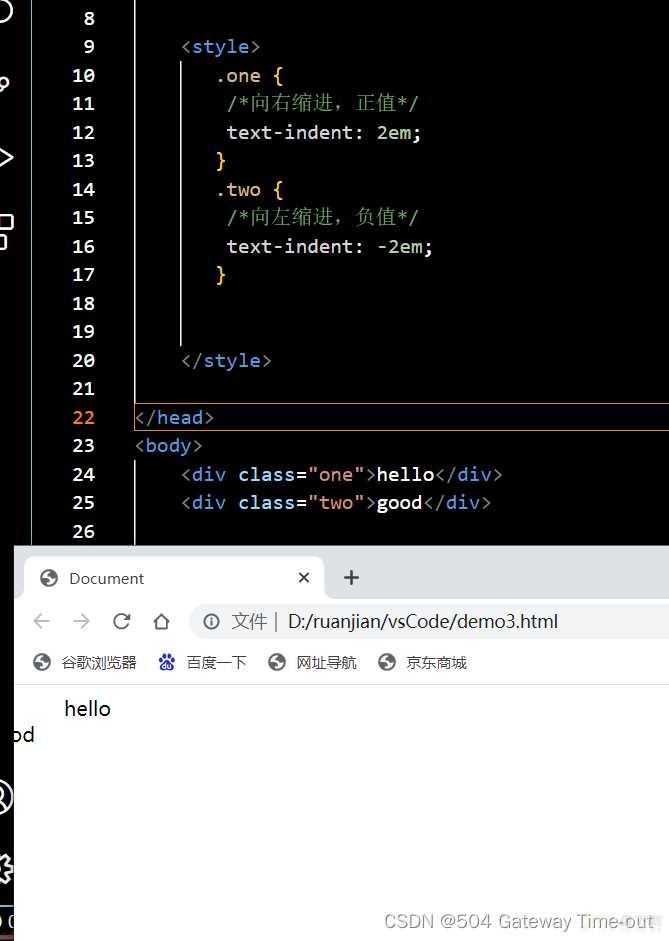
这里文字向左缩进;导致文字显示不完整;
行高设置;
<style>
.one {
line-height: 50px;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>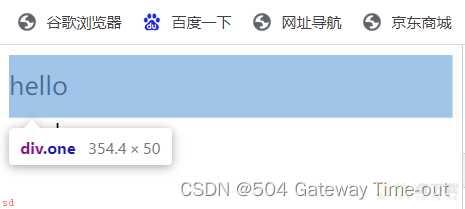

行高实际就是上下文本之间的基线的距离;即文本上边距加上下边距以及字体大小即文本的行高;
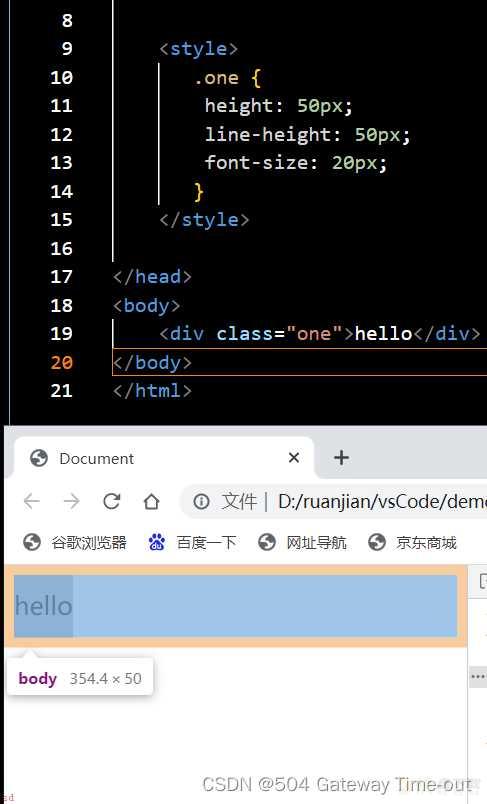
当行高与元素的高度相等时;文字可以居中对齐;
背景颜色;background-color;
<style>
.one {background-color: aqua;
}
/*默认透明;transparent;*/
.two {background-color: transparent;
}
</style>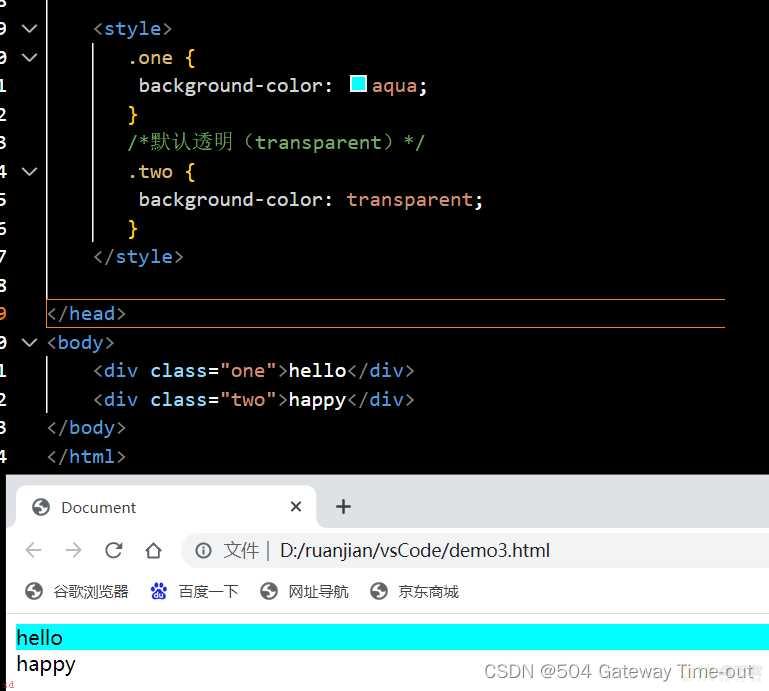
背景图片设置;background-image: url(图片路径);
<style>
.one {background-image: url(2.jpg);
height: 350px;
}
</style>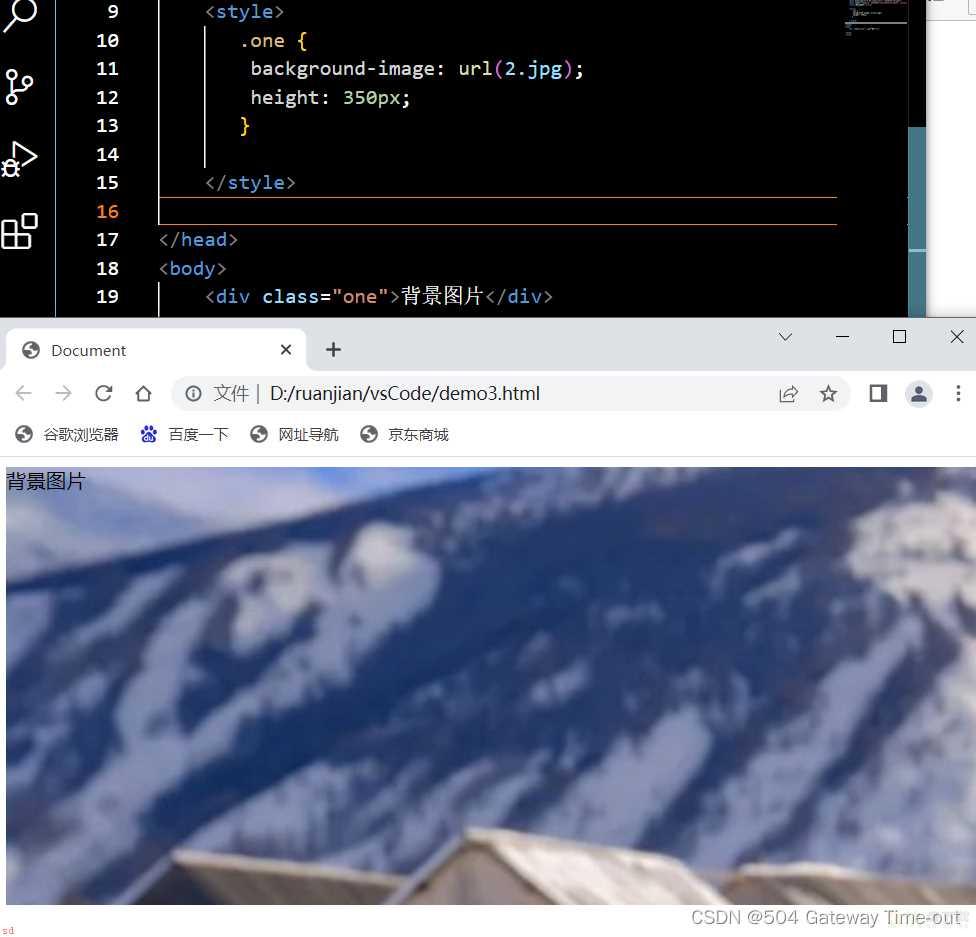
url可以是绝对路径;也可以是相对路径;
背景平铺;background-repeat;
<style>
/*平铺*/
.one {background-image: url(yun.png);
height: 350px;
background-repeat: repeat;
}
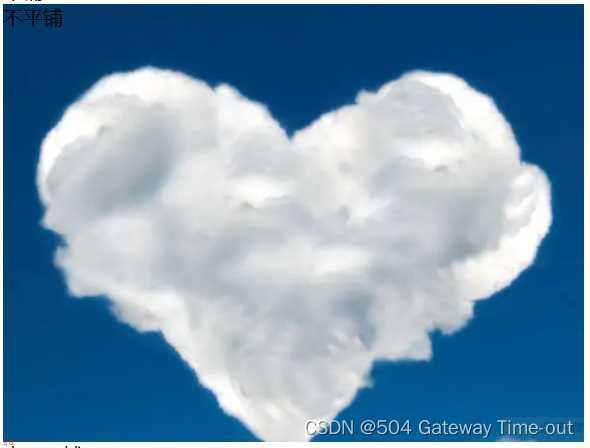
/*不平铺*/
.two {background-image: url(yun.png);
height: 350px;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
}
/*水平平铺*/
.three {background-image: url(yun.png);
height: 350px;
background-repeat: repeat-x;
}
/*垂直平铺*/
.four {background-image: url(yun.png);
height: 700px;
background-repeat: repeat-y;
}
</style>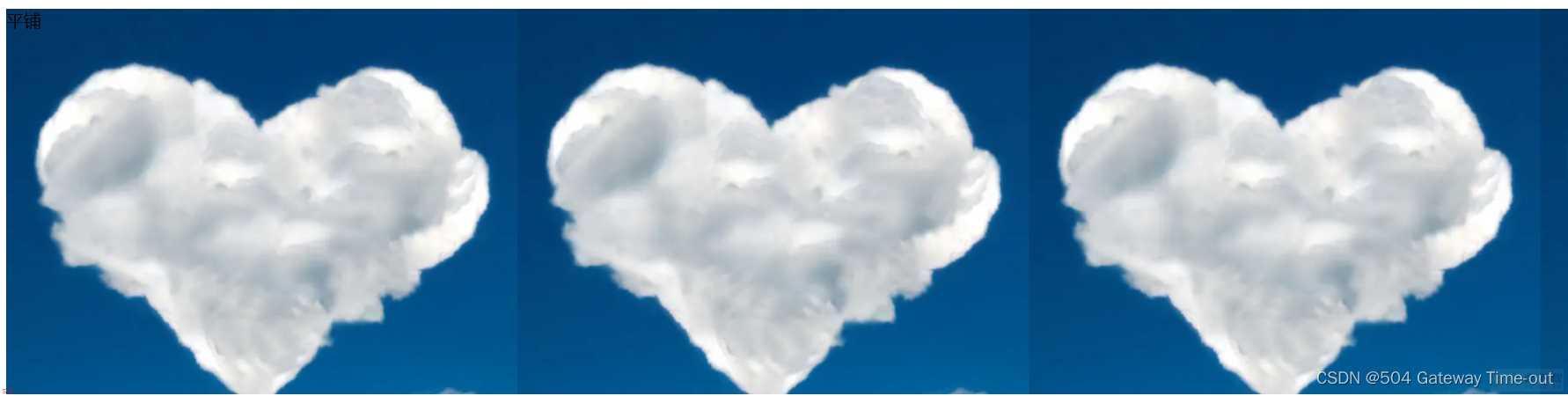
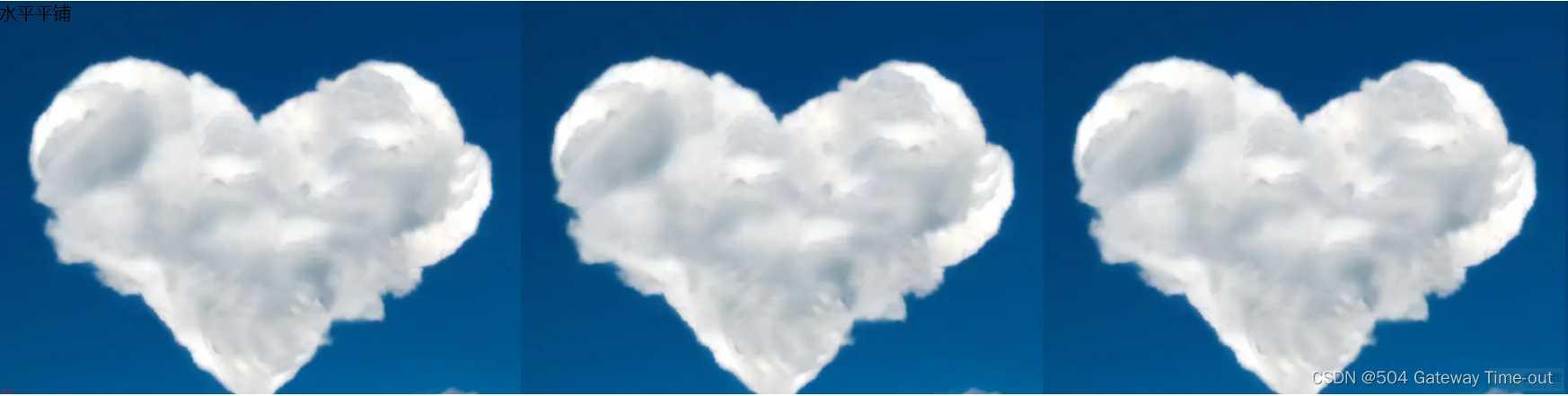
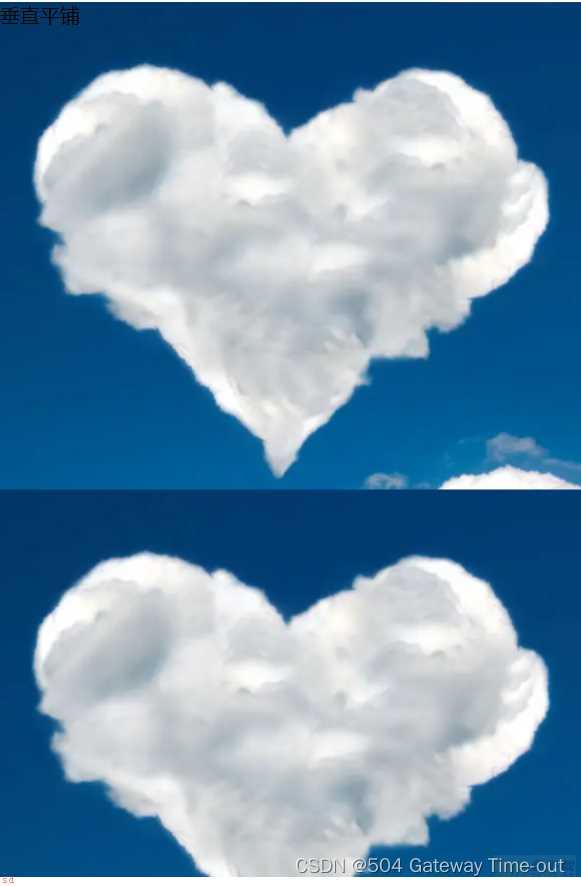



背景位置;background-position
背景位置是以坐标系;左上角为原点;为基准;由x和y2个值来确定;也可以使用方位名词来确定;
方位名词有;top, left, right, bottom;
当x和y都是方位名词时;2个方位名词的顺序等效;
当只指定了一个方位名词;或具体数值;时;第二个默认居中设置;
当x和y都是具体数值时;就是基于原点的位置;
<style>
/*使用方位名词设置;表示左上*/
.one {background-image: url(yun.png);
height: 350px;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: left,top ;
}
/*只指定了一个方向;第二个方向默认垂直居中*/
.two {background-image: url(yun.png);
height: 350px;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: right ;
}
/*使用具体数值确定*/
.three {background-image: url(yun.png);
height: 350px;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: 300,500 ;
}
</style>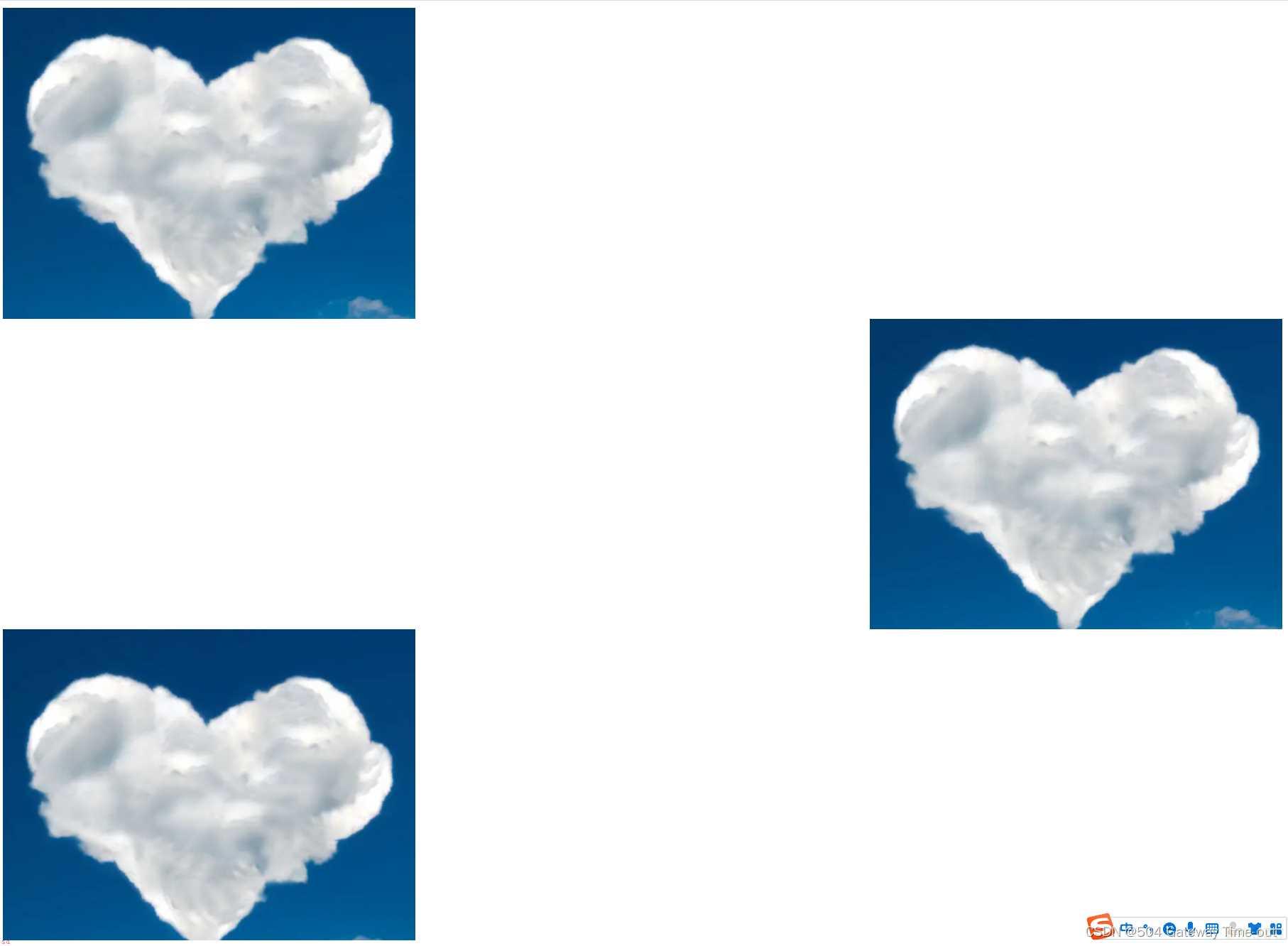
背景尺寸;
可以使用具体的数值来设置;单位为像素;
也可以使用contain或者cover 2个关键词来设置;
<style>
/*contain*/
.one {background-image: url(sky.png);
height: 350px;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: center ;
background-size: contain;
}
/*cover*/
.two {background-image: url(sky.png);
height: 350px;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: center ;
background-size: cover;
}
</style>
cover:缩放背景图片以完全覆盖背景区;可能背景图片部分看不见;
contain:缩放背景图片以完全装入背景区;可能背景区部分空白;
<style>
.one {width: 100px;/*宽高一致;代表是个正方形*/
height: 100px;
border: 2px solid green;/*边线的格式-2个像素的绿色实线*/
/* 用 50% 表示宽度的一半 */
border-radius: 50%
}
.two {width: 200px;/*宽高一致;代表是个正方形*/
height: 100px;
border: 2px dashed black;/*边线的格式-2个像素的黑色虚线*/
/*圆角的弧度设置*/
border-radius: 10px;
}
</style>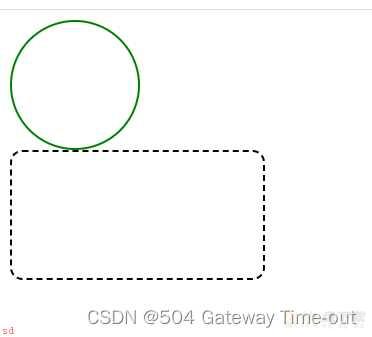
border-radius;通过设置矩形内切圆的半径来控制弧线的程度;
也可以对矩形的四个角分别进行圆角弧度的设置;
块级元素和行内元素都属于CSS中;Html的元素显示模式;
块级元素
块级元素主要有这样几个特点;
块级元素一般都是独占一行;
块级元素的高度、宽度、内外边距、行高都是可以进行设置的;
块级元素的高度默认与父级元素一样宽;
块级元素的内部;可以是块级元素或者行内元素;
常见的块级元素有;标题标签;h1-h6、段落标签;p、无语义标签;div、ul、ol、li;
段落标签p内不可以存放块级元素;
<style>
.one {width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: goldenrod;
}
.two {width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: rgb(32, 71, 83);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--块级元素-->
<div class=;one;>
<div class=;one1;>
hello world
</div>
</div>
<div class=;two;>
<span>happy end</span>
</div>
</body>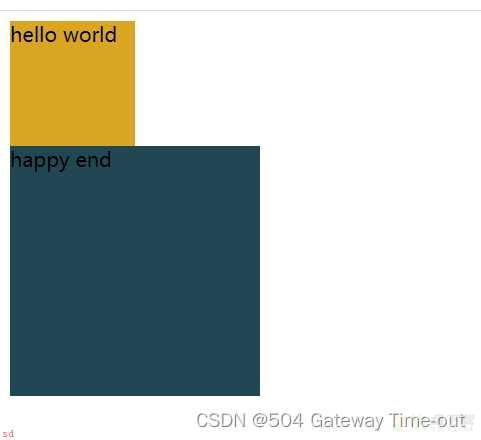
行内元素;
行内元素不独占一行;同一行可以显示多个;
行内元素设置高度;宽度;行高均无效;
行内元素可以设置左右外边距、内边距;上下边距设置无效;
行内元素内部只能有其他行内元素;不可以有块级元素;
常见的行内元素有:a,span,strong,em,u,d等;
<style>
.one {width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: goldenrod;
}
.two {width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: rgb(32, 71, 83);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--行内元素-->
<span>
<span class=;one;>hello world</span>
<span class=;two;>happy end</span>
</span>
</body> 块级元素和行内元素可以使用一定的方法进行转换;即display;
块级元素和行内元素可以使用一定的方法进行转换;即display;
display: block 改成块级元素 [常用];
display: inline 改成行内元素(很少使用)
display: inline-block 改成行内块元素;
我们可以将Html的元素视为一个矩形;即盒子;这个盒子一般包括这样几个部分;
边框;border;、内容;content;、内边距;padding;、外边距;margin;;
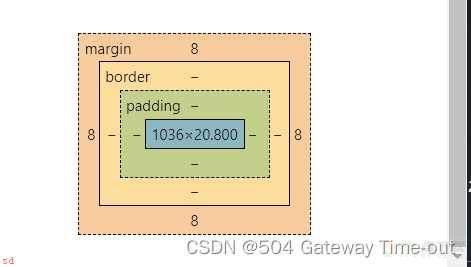
边框;
<style>
div {width: 300px;/*边框宽度*/
height: 100px;/*边框高度*/
background-color: goldenrod;/*边框颜色*/
border-style: none;/*边框样式;无*/
box-sizing: border-box;/*修改浏览器的行为;保证边框的存在不会撑大盒子*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
</body>
内边距;padding;
<style>
div {width: 300px;/*内边距宽度*/
height: 100px;/*内边距高度*/
/*分别给四个方向都加边框*/
padding-top: 3px;
padding-bottom: 3px;
padding-left: 3px;
padding-right: 3px;
}
* {box-sizing: border-box;
}
</style>
内边距的设置可以进行合并;当padding后只有一个变量时;表示四个方向均为该大小;padding后有2个变量时;第一个变量表示上下内边距的大小;第二个变量表示左右内边距的大小;三个变量表示左;上下;右;
外边距;margin
<style>
div {width: 300px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #fff;
}
.one {margin: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class=;one;>hello</div>
<div class=;two;>happy</div>
</body>

 上图1,2表示分别的2个盒子;3表示2个盒子形成的整体;
上图1,2表示分别的2个盒子;3表示2个盒子形成的整体;
外边距也可以进行合并设置或四个方向分别设置;与内边距设置类似;
块级元素的水平居中即让整个盒子位于整个页面的中心位置;与文本的居中不同;也不可混淆;
<style>
div {width: 300px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #fff;
margin: auto;
}
</style>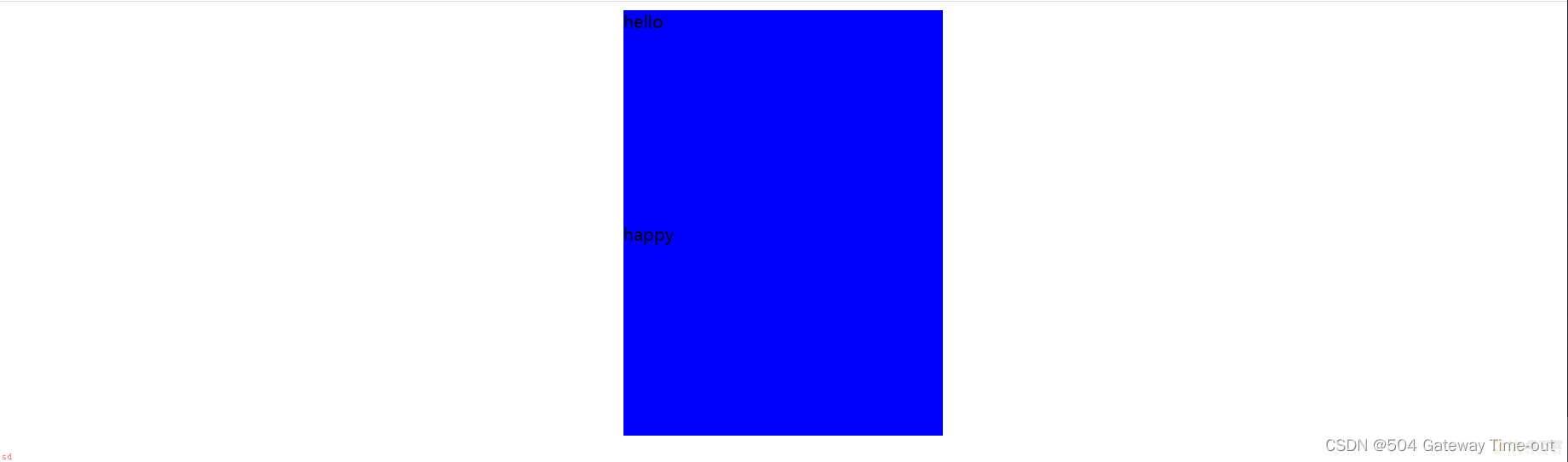
块级元素水平居中即将水平内边距设置为auto;
由于将来我们的网页具体运行在哪个浏览器上是不确定的;而一般情况下浏览器都会默认给元素加上一些样式;像内外边距或者其他元素;为了保证我们的代码在不同的浏览器上可以得到相同的效果;需要使用一些方法来去除这种浏览器默认带来的样式;
* {
margin:0;
padding:0;
}使用通配符即可;
弹性布局;flex布局;即为html的元素指定一个display:flex的属性;即可使元素在任意我们希望的位置出现;
被设置为 display:flex 属性的元素, 称为 flex container;
它的所有子元素立刻称为了该容器的成员, 称为 flex item;
对容器成员的排列;可以横向排列和纵向排列;
横向排列设置;justify-content
<style>
div {width: 100%
height: 500px;
background-color: rgb(97, 97, 219);
/*使成为弹性盒子*/
display: flex;
/*flex-start:位于容器的开头;默认值*/
justify-content: flex-start;
}
div span {width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(201, 162, 162);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<span>happy1</span>
<span>happy2</span>
<span>happy3</span>
</div>
</body>
/*center:位于容器的中央*/ justify-content: center;

/*center:位于容器的末尾*/ justify-content: flex-end;

/*center:在行与行之间留有间隔*/ justify-content: space-between;
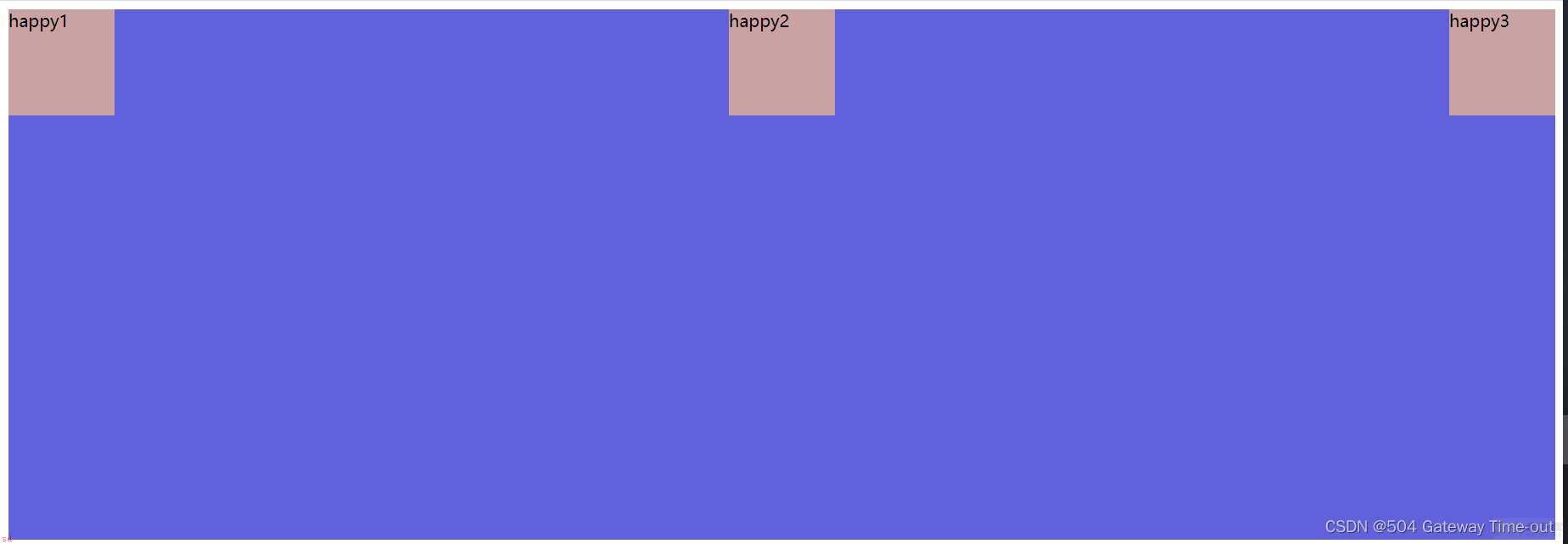
/*center:在行与行之前;之间;之后留有间隔*/ justify-content: space-around;
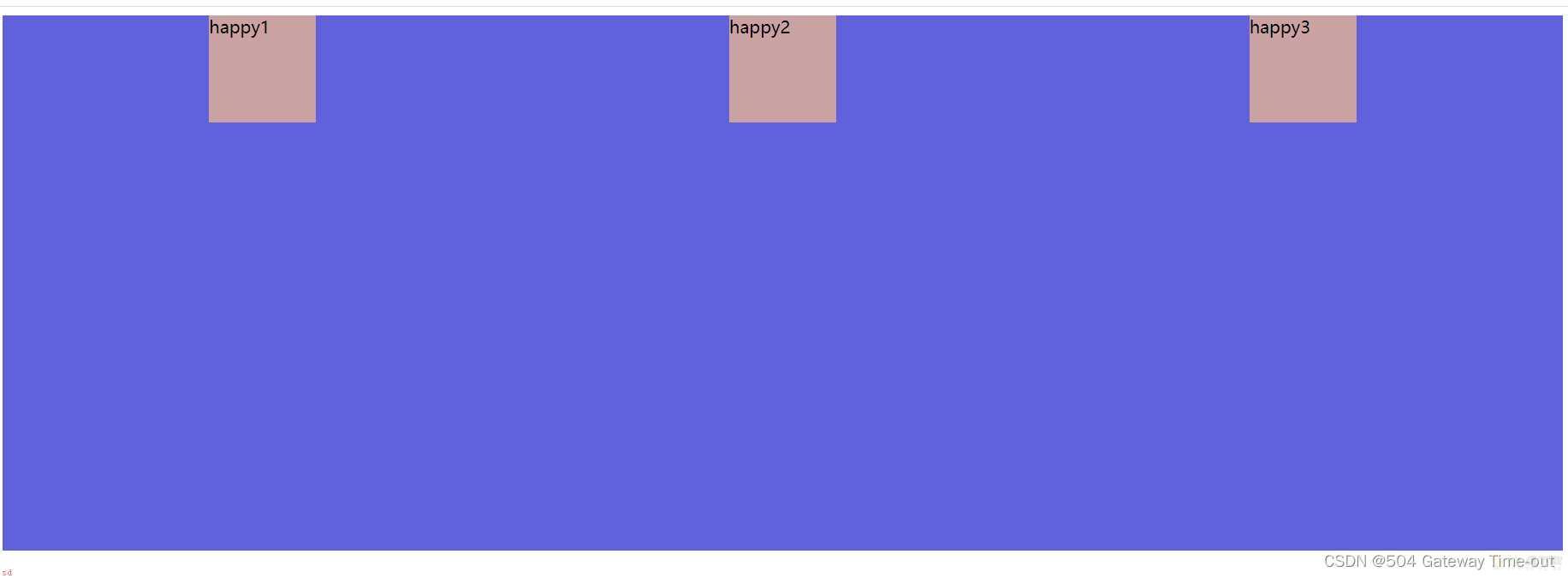
纵向排列设置;align-content
<style>
div {width: 100%
height: 500px;
background-color: rgb(97, 97, 219);
/*使成为弹性盒子*/
display: flex;
/*stretch:纵向拉伸占据剩余空间*/
align-content: stretch;
}
div span {width: 100px;
background-color: rgb(201, 162, 162);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<span>happy1</span>
<span>happy2</span>
<span>happy3</span>
</div>
</body>
更多关于弹性布局纵向设置的知识可以参考官方文档;
垂直居中;
<style>
div {width: 100%
height: 500px;
background-color: rgb(97, 97, 219);
/*使成为弹性盒子*/
display: flex;
justify-content: space-around;
align-items: center;
}
div span {width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(201, 162, 162);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<span>happy1</span>
<span>happy2</span>
<span>happy3</span>
</div>
</body>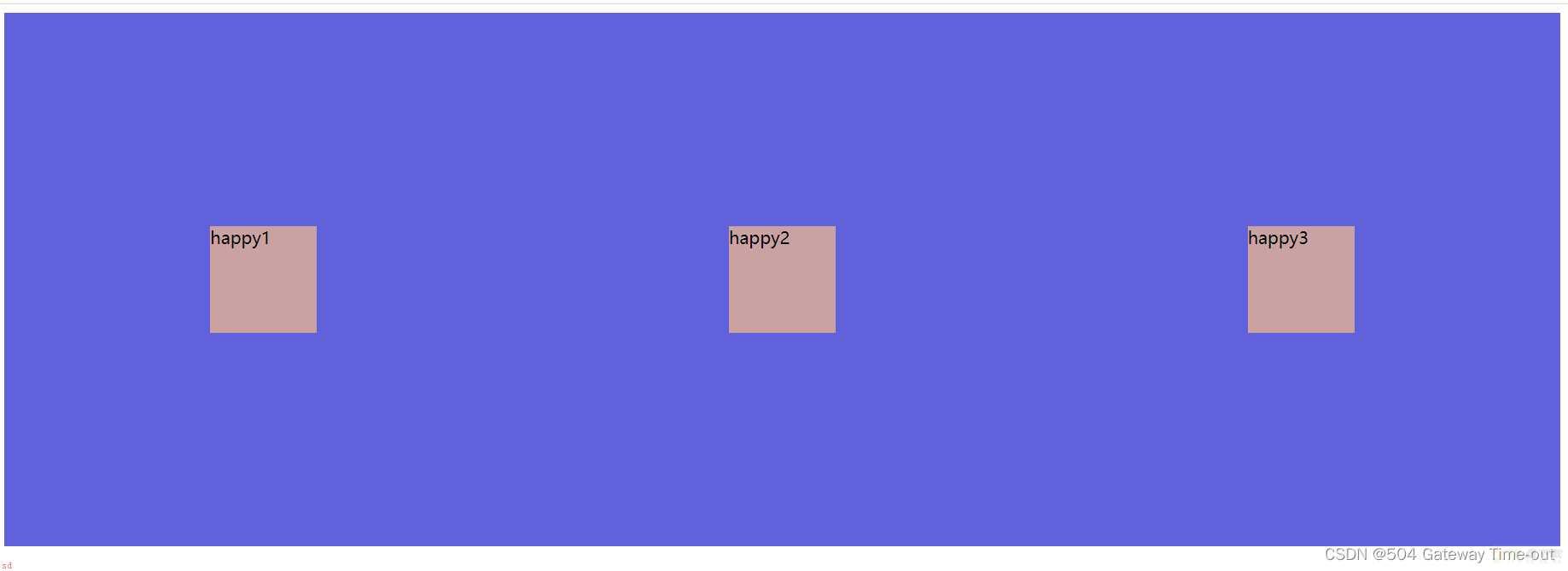
align-items 只能针对单行元素来实现. 如果有多行元素, 就需要使用 item-contents;
这里只是对css知识的简单介绍;更多具体有关CSS的知识依然可以参考官方文档MDNCSS官方文档;
over;

solidworks2020怎么获得下列许可standard?-solidworks2020获得下列许可standard教程攻略
solidworks2020怎么导出二维图?-solidworks2020导出二维图教程攻略